38/25 Timeline of Climate Change: How Earth Went from Ice Age to Global Warming
Posted 5 months ago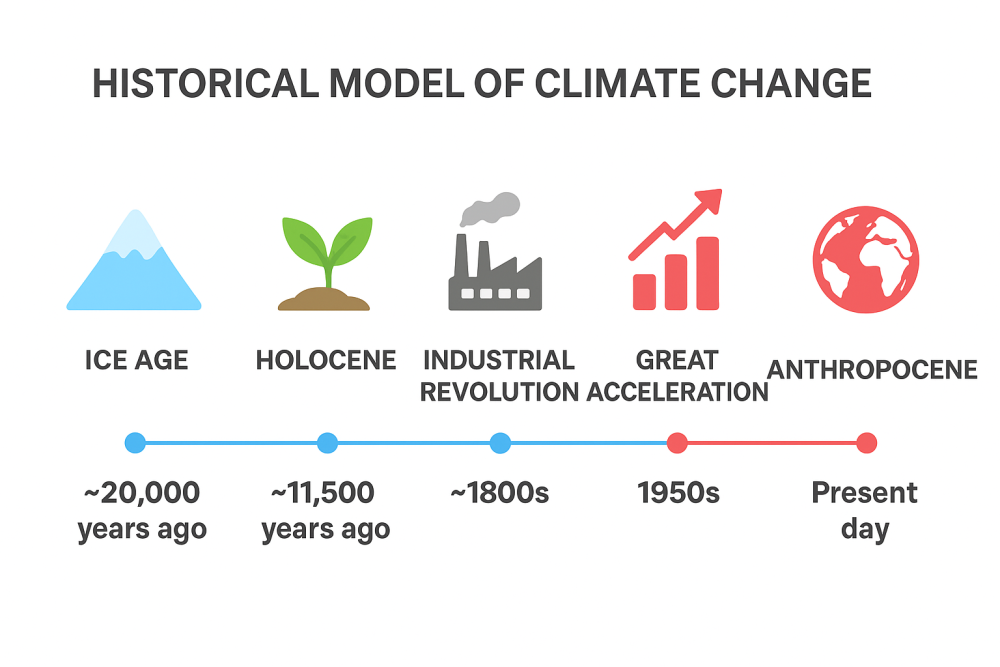
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The history of Earth’s temperature rise tells the story of how our planet has shifted from natural cycles of ice ages and warm periods to a new era primarily shaped by human activity. Earth’s climate remained relatively stable for thousands of years, especially during the Holocene era, which allowed agriculture and civilizations to flourish. However, since the Industrial Revolution in the 1800s, the massive use of fossil fuels has sharply increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This has driven a rapid rise in global temperatures, especially after the 1950s, a period scientists call the “Great Acceleration.” Today, Earth is warming faster than ever, pushing the planet into the Anthropocene, an era defined by human impact on climate. Let's see how the Earth moved from ice age to global warming.
Ice Age (~20,000 years ago):
Earth was at the peak of the last Ice Age with maximum glaciation.
The climate began to warm gradually afterward.
Holocene Era (~11,500 years ago):
The climate warmed abruptly, a sudden shift that led to a relatively warm, steady phase.
This stable climate shifted the Agricultural Revolution from hunter-gatherers to farming societies.
The Holocene became the foundation for human civilization.
Industrial Revolution (~1800s):
Marked the beginning of large-scale fossil fuel use (coal, oil, gas).
Rapid industrialization and burning fossil fuels introduced large amounts of carbon dioxide and pollutants into the atmosphere.
This period marks the start of the Anthropocene, the human-driven changes.
Post–World War II (1950s onward):
Period known as the Great Acceleration:
Massive growth in population, GDP, vehicles, water, and food consumption.
Sharp rise in fossil fuel use and greenhouse gas emissions.
Observable Impacts of Global Warming:
- CO₂ concentrations spiked after 1950.
- Global temperatures increased about 20 years later.
- Ozone depletion became a crisis in the 1980s.
- Biodiversity loss and species extinction have accelerated worldwide.
- Pollution spreads globally across the air, water, and ecosystems from the Arctic to the Antarctic.
Current Anthropocene Era (Present Day):
Human activity has warmed the planet by about 1°C already.
If trends continue (“business as usual”), global warming is projected to rise 2–4°C.
This warming exceeds the natural range of past interglacial periods.
Let's leave better environments for coming generations
The current climate is the warmest in at least 20,000 years.
If warming continues past 2°C, humanity and living survival will be a challenge.
Important to Understand
- Climate naturally shifts between glacial (cold) and interglacial (warm) cycles, but human activity has pushed it beyond natural patterns.
- Human-made warming is faster and more extreme than in recent geological history.
- This raises urgent societal and economic concerns if business continues as usual.
The above information has been organized for you by the University of Southern Punjab Multan, a best university located in Multan, Pakistan
REFERENCE AND ADDITIONAL READING
Bending the Curve: Climate Change Solutions - Open Textbook Library