39/25 Unveiling the Mystery: How the Greenhouse Effect Fuels Global Warming and Climate Change
Posted 5 months ago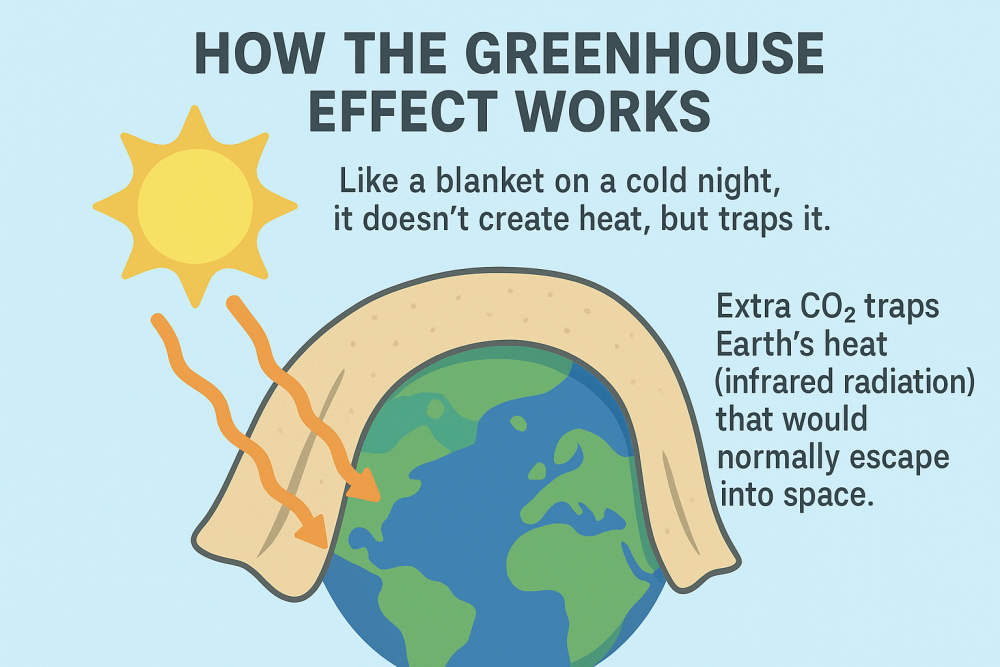
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The greenhouse effect works like a blanket on a cold night. The blanket doesn’t make heat by itself, it just traps the warmth that would otherwise escape. Similarly, Earth’s atmosphere naturally traps some of the sun’s heat, keeping our planet warm enough for life.
But when humans add extra carbon dioxide (CO₂) and other gases from burning coal, oil, and gas, the “blanket” gets much thicker. This traps more heat than usual, causing Earth’s temperature to rise. The result is global warming, leading to hotter days, stronger storms, melting ice, and rising seas.
In short: More CO₂ means a thicker blanket and a hotter planet.
Earth’s atmosphere is a thin protective blanket
It contains gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor that make life possible. Water vapor forms clouds and rain, while ozone protects us from harmful UV rays.
Why this blanket matters?
- Earth would be frozen without greenhouse gases (like CO₂ and water vapor). Carbon dioxide traps heat and keep the Earth warmer.
- Earth would be too hot without clouds, ice, and snow reflecting sunlight.
- The atmosphere keeps Earth’s temperature “just right” for life.
Human impact since the Industrial Revolution
- In ~240 years, humans have released 2 trillion tons of CO₂.
- About 45% still lingers in the atmosphere, forming a human-made “blanket.”
- This CO₂ blanket weighs about 930 billion tons like 450 billion cars running nonstop around Earth.
Air moves pollution around the globe fastly
- Scientific studies show that pollutants from China can reach the U.S. in 4 days.
- U.S. air can cross the Atlantic in 3 days.
- South American air can reach Antarctica in 3–4 days.
Lesson: Pollution anywhere affects the entire planet.
How the greenhouse blanket works?
- Like a blanket on a cold night, it doesn’t create heat but traps it.
- Extra CO₂ traps Earth’s heat (infrared radiation) that would typically escape into space. This is the greenhouse effect.
Natural greenhouse effect vs. artificial
Natural greenhouse gases keep Earth livable. But humans have thickened the blanket too much, upsetting Earth’s balance.
Energy/Heat balance of Earth
- Sunlight enters Earth (100%), and about 30% bounces back (reflected by clouds, snow, ice).
- The remaining 70% heat warms Earth.
- Normally, Earth re-emits this heat as infrared radiation back into space, maintaining a balance of energy. This balance is crucial for Earth's temperature to remain stable.
Extra CO₂ traps more heat → energy imbalance → global warming.
How much heat are we trapping?
As of 2010, 860 terawatts of extra energy were trapped.
That equals:
70 times all the world’s energy use.
Or running 14 trillion 60-watt light bulbs every second, nonstop.
Result: Earth is heating everywhere
The effects are already visible in extreme weather such as more frequent and severe hurricanes, melting ice in the polar regions, rising seas that threaten coastal communities, and shifting climates that disrupt ecosystems and agriculture.
The above information has been organized for you by the University of Southern Punjab Multan, a best university located in Multan, Pakistan
REFERENCE AND ADDITIONAL READING
Bending the Curve: Climate Change Solutions - Open Textbook Library