67/25 Lecture 2 : Introduction to Environmental Science - Course Learning Objectives (CLOs)
Posted 3 months ago
Video for this lecture is available HERE
In the Introduction to Environmental Science, class we embark on an intellectual and moral journey, one that takes us beyond textbooks and into the very fabric of life on our planet. Introduction to Environmental Science is not just a course about ecosystems, pollution, or sustainability, it is the story of our relationship with the Earth.
For billions of years, our planet has maintained a delicate balance that sustains all forms of life. The air we breathe, the water we drink, and the soil that nourishes our crops are all part of a finely tuned system of interactions. Humanity, though relatively new in Earth’s history, has become a dominant force capable of shaping the environment on a global scale.
This dual role as beneficiaries and disruptors of nature’s balance defines the essence of environmental science. We study not only how the environment sustains us but also how our actions, technologies, and social systems, in turn, alter the environment.
Throughout this course, we will address questions that sit at the intersection of science, ethics, and humanity:
- How does climate change reshape our world?
- Why is biodiversity essential for the stability of ecosystems?
- How do economic policies influence environmental justice?
- And most importantly, what ethical responsibilities do we bear as stewards of this planet?
By the end of this course, you will develop a holistic understanding of scientific, social, and moral aspects and how human and natural systems are intertwined. You will begin to see that environmental science is not merely an academic discipline but a moral imperative, a call to rethink how we live, consume, and coexist with nature.
Course Learning Objectives
By the end of this course, students will be able to
- Understanding the Importance of Environmental Science in Human Life
- Recognize how environmental systems, water, soil, and biodiversity support human existence.
- Appreciate the interdependence between nature and society.
- Evaluate the Impact of Environmental Science on Society
- Examine how environmental awareness influences policy, economics, technology, and social well-being at local and global scales.
- Analyze Global Environmental Phenomena
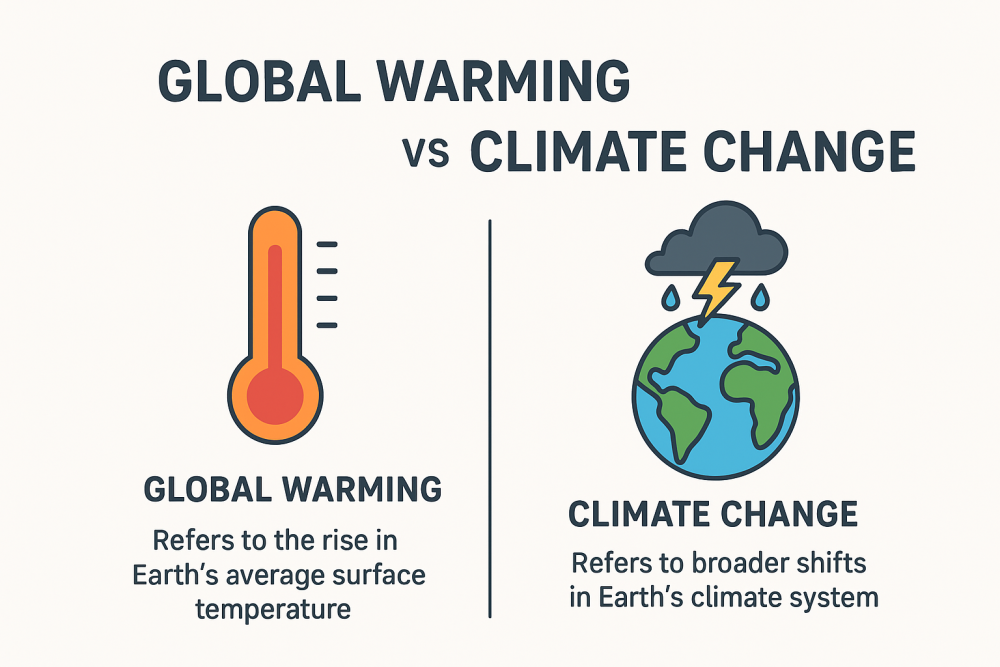
- Explore the scientific foundations and societal implications of climate change, global warming, and pollution.
- Identify Challenges to Biodiversity Conservation
- Assess how human activities threaten ecosystems and what strategies can be used to protect species and habitats.
- Examine National, Regional, and Global Challenges for Sustainable Development
- Critically assess Pakistan’s ecological and developmental context within the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) framework.
- Relating Environmental Issues to Human Well-being
- Connect environmental conditions to health, food security, poverty, energy, and cultural resilience.
- Reflect on Moral and Ethical Responsibilities
- Evaluate ethical dimensions of human choices and our responsibility as custodians of the Earth.
The University of Southern Punjab, Multan, Pakistan, recognizes education as a shared social responsibility and a powerful instrument for community uplift. The University reinforces its commitment to environmental awareness, sustainable living, and civic engagement by offering the Introduction to Environmental Science course to students and the general public. This initiative enriches students’ understanding of how natural systems support life and empowers the wider community to make informed decisions for a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future. Through this program, USP takes a leading role in transforming knowledge into action, inspiring and motivating the collective well-being of South Punjab and beyond.